리눅스 쉘(shell)에서 디렉토리 구조를 확인하고 싶다면 ls 명령어를 이용해 확인할 수 있습니다. 하지만 디렉토리가 나열되어 보이기 때문에 계층 구조를 확실하게 구분짓지 못해 사용자 입장에서는 가독성이 떨어지게 되는데요.
이렇게 보기 힘든 디렉토리 구조를 좀더 편하게 확인할 수 있는 tree 패키지를 소개합니다.
# apt-get install tree # 우분투 # yum install tree # CentOS # tree
관리자 권한을 가진 상태에서 tree 패키지를 설치한 후 다음 tree 명령어를 입력하면 현재 위치한 하위 디렉토리 및 파일을 구조적인 형태로 보여줍니다.
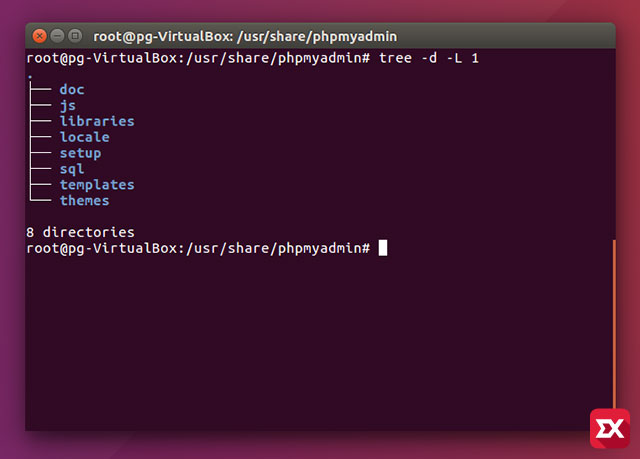
# tree -d -L 1
만일 디렉토리만 확인하고 싶다면 -d 옵션을 이용해 필터링한 다음 출력할 수 있습니다. -L 옵션 같은 경우 하위 디렉토리 레벨을 지정해 출력하게 됩니다.
이밖에도 아래와 같은 옵션이 있으니 응용해서 사용하면 좀더 직관적으로 디렉토리 구조를 확인할 수 있습니다.
usage: tree [-acdfghilnpqrstuvxACDFJQNSUX] [-H baseHREF] [-T title ] [-L level [-R]] [-P pattern] [-I pattern] [-o filename] [--version] [--help] [--inodes] [--device] [--noreport] [--nolinks] [--dirsfirst] [--charset charset] [--filelimit[=]#] [--si] [--timefmt[=]<f>] [--sort[=]<name>] [--matchdirs] [--ignore-case] [--] [<directory list>] ------- Listing options ------- -a All files are listed. -d List directories only. -l Follow symbolic links like directories. -f Print the full path prefix for each file. -x Stay on current filesystem only. -L level Descend only level directories deep. -R Rerun tree when max dir level reached. -P pattern List only those files that match the pattern given. -I pattern Do not list files that match the given pattern. --ignore-case Ignore case when pattern matching. --matchdirs Include directory names in -P pattern matching. --noreport Turn off file/directory count at end of tree listing. --charset X Use charset X for terminal/HTML and indentation line output. --filelimit # Do not descend dirs with more than # files in them. --timefmt <f> Print and format time according to the format <f>. -o filename Output to file instead of stdout. -------- File options --------- -q Print non-printable characters as '?'. -N Print non-printable characters as is. -Q Quote filenames with double quotes. -p Print the protections for each file. -u Displays file owner or UID number. -g Displays file group owner or GID number. -s Print the size in bytes of each file. -h Print the size in a more human readable way. --si Like -h, but use in SI units (powers of 1000). -D Print the date of last modification or (-c) status change. -F Appends '/', '=', '*', '@', '|' or '>' as per ls -F. --inodes Print inode number of each file. --device Print device ID number to which each file belongs. ------- Sorting options ------- -v Sort files alphanumerically by version. -t Sort files by last modification time. -c Sort files by last status change time. -U Leave files unsorted. -r Reverse the order of the sort. --dirsfirst List directories before files (-U disables). --sort X Select sort: name,version,size,mtime,ctime. ------- Graphics options ------ -i Don't print indentation lines. -A Print ANSI lines graphic indentation lines. -S Print with CP437 (console) graphics indentation lines. -n Turn colorization off always (-C overrides). -C Turn colorization on always. ------- XML/HTML/JSON options ------- -X Prints out an XML representation of the tree. -J Prints out an JSON representation of the tree. -H baseHREF Prints out HTML format with baseHREF as top directory. -T string Replace the default HTML title and H1 header with string. --nolinks Turn off hyperlinks in HTML output. ---- Miscellaneous options ---- --version Print version and exit. --help Print usage and this help message and exit. -- Options processing terminator.